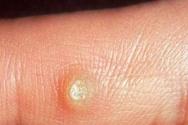
Increasing the productivity of mold fungi producing. Molds, what are they and how can they be useful? Increasing the productivity of molds that produce antibiotics
Mold and mildew, which are essentially the same thing, are organisms that were among the first to appear on planet Earth. They are unpretentious when it comes to living conditions, and they are also very diverse! Currently, about a hundred thousand species of fungi have been described (and it is estimated that there are more than a million of them on Earth). About 2/3 of them are yeast and mold fungi.
Despite the variety of species, molds have their own characteristics.
They will be discussed in the next section.
Micromycetes or molds constitute a group of lower fungi. It’s difficult to see what mold looks like, since it, unlike butter and chanterelles that are familiar to our eyes, does not have a large fruiting body.
What does mold consist of? The vegetative body of a mold fungus is a thin, branched mycelium (mycelium), consisting of a single cell that has a large number of nuclei. From the mycelium grows a whole “field” of thin branching threads - hyphae. They are located on the surface or inside the object that the mold has chosen.
In most cases, the mycelium of mold fungi is of impressive size and occupies a huge area.
Any type of mold has its place in the natural environment and reproduces successfully in it. To do this, they don’t even need a special, “romantic” atmosphere. All they need to grow and develop is high temperature and high humidity. The fact that these organisms do not have the need to search for food sets them apart from their “relatives” and allows them to release mold spores in almost any conditions.
Interesting facts about mold
Molds also include rare, exotic species. Mushroom pickers tirelessly hunt for some of them (for example, they are interested in Hypomyces latiformis, a large mold fungus that settles on fruiting bodies other mushrooms, after which the latter stop growing). The remaining varieties are not of particular value to mushroom pickers (black aspergillus, gray botrytis and others).
As for size, mushrooms show diversity here too. They can be larger than a watermelon, growing up to 1 meter in diameter, or they can be so small that they can only be seen using special instruments (for example, a microscope). We are, of course, not talking about a massive accumulation of such small fungi - their colonies are visible to the naked eye.
Mushrooms are special “plants” that do not have chlorophyll. Due to its absence, mushrooms, unlike higher flowering plants (moss, algae and ferns), cannot absorb carbon dioxide from the air and create the nutrients they need. In short, mushrooms are heterotrophs; they (like animals and people, by the way) feed on ready-made organic substances.
There are a huge number of types of mold fungi. Each species is often further divided into various subspecies. Therefore, it is difficult to classify a certain variety into any one group based solely on color. Even the same seemingly same penicillium can be of different colors depending on which subspecies of one large group it belongs to.
Nevertheless, let's try to understand the “varieties” of molds, and at the same time learn more about some of them.
Black
This color depends not only on the type of mold, but also on the stage of development at which it is currently located. The surface of the material, “captured” by mold fungi, also plays an important role.
The following species are often “painted” black:

So, we have more or less sorted out the black mold that everyone is so afraid of. Now let's quickly look at the other colors.
Gray
 Saprophytic mold fungi, feeding on dead organic particles, harm not only the berries and fruits that they have captured, but also the human body. Gray mold looks like simple plaque. It settles on surfaces of any material, food, etc.
Saprophytic mold fungi, feeding on dead organic particles, harm not only the berries and fruits that they have captured, but also the human body. Gray mold looks like simple plaque. It settles on surfaces of any material, food, etc.
Houseplants can also suffer from gray mold, as it also infects flower seeds.
White
 White mold does not scare people as much as black mold, but this does not mean that it is beneficial and not destructive. Often found on the ground, trees and plants, cheeses and baked goods. In homes, mucor, or white capitate mold, usually appears in flower pots, and extremely rarely on walls.
White mold does not scare people as much as black mold, but this does not mean that it is beneficial and not destructive. Often found on the ground, trees and plants, cheeses and baked goods. In homes, mucor, or white capitate mold, usually appears in flower pots, and extremely rarely on walls.
People often confuse efflorescence (discoloration) on walls with ordinary white mold. It is easy to distinguish efflorescence from mold. The first crumbles in your hands because it has a crystalline structure, while the second kneads. Before such a check, of course, you need to wear gloves; you should not take mold mushrooms with your bare hands.
Will save you from white mold in a pot lemon acid- She needs to water the soil regularly.
Pink
 Mold, which looks like a fluffy pink cloud, does not attack building materials as often as some other types of molds. Much more often it appears on plant debris and rotting products (spoiled fruits, vegetables or even cereals that were stored in unsuitable conditions).
Mold, which looks like a fluffy pink cloud, does not attack building materials as often as some other types of molds. Much more often it appears on plant debris and rotting products (spoiled fruits, vegetables or even cereals that were stored in unsuitable conditions).
Pink mold is not particularly dangerous, but it is still better to throw away food that is covered with it.
 Blue
Blue
Blue mushrooms, known as “noble mold,” are rare guests in private houses and apartments; much more often they settle on trees. Blue mold is not particularly dangerous for humans. Moreover, sometimes it even brings benefits. For example, it is used to make those most exquisite varieties of cheese.
Green
 Everyone has probably seen an onion at least once in their life (but it also affects garlic) covered with an unpleasant green-blue coating. These are representatives of the genus Penicillium (most often they are P. expansum Thom., P. glaucum Link).
Everyone has probably seen an onion at least once in their life (but it also affects garlic) covered with an unpleasant green-blue coating. These are representatives of the genus Penicillium (most often they are P. expansum Thom., P. glaucum Link).
However, there are also useful green molds, for example, from the genus Trichoderma (in particular, Trichoderma viride). It is used to make Trichodermin, a substance that protects plants from other fungi and various diseases.
About efflorescence, as promised.
Efflorescence (efflorescence)
 This is a white (sometimes, very rarely, colored) salt or alkaline coating that appears on the walls. It is based on insoluble sulfates, carbonates and silicates. Formed due to the movement of liquid along with salts inside materials. The water evaporates and the salts crystallize, resulting in a white coating on the wall, which is often confused with ordinary white mold.
This is a white (sometimes, very rarely, colored) salt or alkaline coating that appears on the walls. It is based on insoluble sulfates, carbonates and silicates. Formed due to the movement of liquid along with salts inside materials. The water evaporates and the salts crystallize, resulting in a white coating on the wall, which is often confused with ordinary white mold.
Most often, efflorescence appears on facades made of brick and concrete. Crystallization also occurs inside the material, causing it to crack and collapse.
A little more about mushrooms...
 Molds live not only around us, but also on us! Fungi, considered dermatophytic, prefer to colonize the upper stratum corneum of human skin.
Molds live not only around us, but also on us! Fungi, considered dermatophytic, prefer to colonize the upper stratum corneum of human skin.
By the way, about the head!
There is another resident in the hair - a fungus. Malassezia. Representatives of this genus live in the mouths of hair follicles, feeding on what remains after the breakdown of fatty acids. Under certain conditions, they can transform from the usual form into a pathogenic (pathogenic) form, causing corresponding inflammatory processes.
Some features of the reproduction and “life” of molds
Fungi can exist both in soil and on water. ( You might be interested - . ) They are found everywhere: in fields and forests, mountain valleys and sandy areas!
Numerous spores, with the help of which fungi reproduce, are present in huge quantities in the air. Sometimes the air flow lifts them tens of kilometers in height or carries them a hundred kilometers into the distance. The record height at which fungal spores were found is 33 kilometers.
Sometimes molds seem to come out of nowhere. So, if you hold a sterile bowl with a suitable medium in an open space, then soon fungal spores will fall onto its surface along with dust and bacteria. After some time, the tiny spores will turn into velvet cushions of mold, which will have different colors and reach several centimeters in diameter.
Surprisingly, the concentration of spores floating in the air is much higher indoors than in open areas.
Fungal spores in the soil are carried along with dust by the wind. So many of them end up in a favorable environment: in food, on the surface of some body of water, plant leaves, or the soil in which they are located, in the respiratory system and on the skin of humans and animals. Some spores, when entering the human body (especially in large quantities), cause various types of diseases.
If we talk specifically about methods of reproduction, there is a sexual, vegetative and asexual method. Fungi can reproduce in all three ways, depending on the class they belong to.
The sexual method (inherent exclusively to higher fungi) involves the union of germ cells and thus the formation of a zygote. With the vegetative method, parts of the mycelium are separated, which can exist independently (such budding also occurs in yeast).
We will not consider these methods of reproduction in more detail, because we are interested in mold fungi. By the way, they reproduce in the last, asexual way or, in other words, with the help of spores.
How exactly are disputes formed? There are two ways:
- Spores are waiting in the wings inside a single cell - a sporangium, which can simultaneously contain up to 10 thousand spores! When the sporangium matures, it opens and the spores are carried away by air or water currents (example: mucor).
- Spores are formed by cells at the ends of filaments - hyphae, forming chains. The last spores in the chain break off and germinate after finding a favorable environment (example: penicillium, aspergillus).
 In addition to the fact that molds easily spread on their own, they are also grown artificially. More precisely, they do not grow, but change existing forms... How and why? To get more benefit, of course! Yes, mold not only causes harm and destroys everything around you, it can heal and even save lives.
In addition to the fact that molds easily spread on their own, they are also grown artificially. More precisely, they do not grow, but change existing forms... How and why? To get more benefit, of course! Yes, mold not only causes harm and destroys everything around you, it can heal and even save lives.
Thus, increasing the productivity of molds that produce antibiotics is achieved through artificial mutagenesis. In other words, changes are made to the DNA structure artificially to ensure maximum performance.
What other benefits are derived from molds? This is the next section.
How and why are mold fungi used?
Some “varieties” of molds are actively used in medicine and the food industry.
With the help of yeast - microscopic fungi that do not have a developed mycelium and grow as individual or linked swollen cells - they make alcoholic drinks(beer, wine), bake bakery products, produce sausage products, prepare sauerkraut and pickle cucumbers.
In winemaking, special attention is paid to mold fungi. The grapes, covered with a sufficient amount of mold, are harvested at a certain time and put into production - the production of elite dessert wines. Gray botrytis (lat. Botrýtis cinérea) is an imperfect stage of mold fungus that constantly lives in the soil and on plant debris, causing the appearance of gray rot on plants - increases the concentration of sugar in grapes, making the taste of the drink more intense.
 In Europe they love cheese with noble mold (brie, Camembert, French Roquefort, English Stilton, Italian Gorgonzola, Danish blue cheese - Danablue). Blue cheese first appeared a couple of thousand years ago. Before, to prepare it, fresh bread were left in the cave for several weeks. After this, the bread, already fairly moldy, was dried, thoroughly crushed and the resulting powder was added to the cheese. Nowadays, of course, no one does this, and edible species fungi are grown in laboratories.
In Europe they love cheese with noble mold (brie, Camembert, French Roquefort, English Stilton, Italian Gorgonzola, Danish blue cheese - Danablue). Blue cheese first appeared a couple of thousand years ago. Before, to prepare it, fresh bread were left in the cave for several weeks. After this, the bread, already fairly moldy, was dried, thoroughly crushed and the resulting powder was added to the cheese. Nowadays, of course, no one does this, and edible species fungi are grown in laboratories.
When it comes to agriculture, molds are more of a pest than something beneficial. However, there are exceptions to everything. For example, some varieties of Fusarium (despite the fact that because of its other varieties, plants rot and animals get sick) living in the soil, on the roots of plants (for example, wheat) have a positive effect on the development of the plant, enhancing its growth.
In Eastern countries, some types of mold have long been used in production soy products food and various sauces.
The dreaded black mold is used as the main ingredient in the production of citric acid.
Mold is an amazing “thing”; it can either save a person’s life or take it away.
 Of course, it is also necessary to pay tribute to the first antibiotic - penicillin. How was it created? This happened in September 1928, and completely by accident. Scottish biologist Alexander Fleming had an assistant. One day, leaving the laboratory in the evening, he forgot to close the window for the night. And in the morning it was noticed that the samples of staphylococci, which were in an open container, were covered with unknown spores. The “spoiled” material was almost thrown away, but at the last moment they decided to study it under a microscope. As it turned out, the spores landing directly on the bacteria killed them, thus preventing further reproduction.
Of course, it is also necessary to pay tribute to the first antibiotic - penicillin. How was it created? This happened in September 1928, and completely by accident. Scottish biologist Alexander Fleming had an assistant. One day, leaving the laboratory in the evening, he forgot to close the window for the night. And in the morning it was noticed that the samples of staphylococci, which were in an open container, were covered with unknown spores. The “spoiled” material was almost thrown away, but at the last moment they decided to study it under a microscope. As it turned out, the spores landing directly on the bacteria killed them, thus preventing further reproduction.
Later studies proved that mold fungi do not neutralize all microbes, but only some, mainly pathogenic ones. Fleming isolated an active substance from mold fungi that destroyed bacterial cells and called it penicillin (in honor of the miraculous mold fungi). The work was published in 1929. However, the scientist did not expect that it would be so difficult to obtain penicillin in its pure form. His initiative was continued by Howard Florey and Ernst Boris Chain, they developed several methods for purifying penicillin.
Mass production of penicillin began during World War II.
In 1945, Fleming, Florey and Chain received the Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology.
The properties of penicillin were appreciated and began to be used in the treatment of various bacterial infections.
1) spores 2) seeds 3) cysts 4) buds
2. An organism whose homologous chromosomes contain genes for dark and light hair color is
1) homozygous
2) heterozygous
3) haploid
4) polyploid
3. The endocrine glands include
1) salivary glands and stomach glands
2) pituitary gland and thyroid gland
3) sweat glands and intestinal glands
4) lacrimal glands and liver
4.Which of the following values blood pressure Can this be considered a sign of hypertension in humans?
1) 170/100 mm Hg. Art.
2) 120/70 mm Hg. Art.
3) 110/60 mm Hg. Art.
4) 90/50 mm Hg. Art.
5.An example of geographic speciation is the formation of species
1) finches living on the Galapagos Islands
2) tits feeding on different foods in a common area
3) sparrows living in different areas of the city
4) perches living at different depths of the reservoir
6.Natural selection, as opposed to artificial,
1) carried out by a person based on his needs
2) leads to the creation of new varieties
3) occurs over millions of years
4) leads to the creation of new breeds
7. The appearance of dark-colored butterflies in a population of light-colored individuals of the birch moth as a result of hereditary variability is called
1) industrial melanism
2) imitative resemblance
3) mimicry
4) warning paint
An example of idioadaptation is
1) the occurrence of the sexual process in plants
2) formation of fruits in angiosperms
3) the appearance of five-fingered limbs in vertebrates
4) the formation of various body shapes in fish
9.What device helps cool plants when the air temperature rises?
1) decrease in metabolic rate
2) increase in the intensity of photosynthesis
3) increased water evaporation
4) decrease in breathing intensity
10. Mushrooms in the forest ecosystem are classified as decomposers, since they
1) consume ready-made organic substances
2) synthesize organic substances from minerals
3) decompose organic substances to minerals
4) carry out the circulation of substances
11. One of the provisions of the teachings of V.I. Vernadsky’s statement about the biosphere is based on the following statement:
1) living organisms are characterized by growth and development
2) all living organisms form species
3) living organisms are connected to their environment
4) living matter - the totality of living organisms on Earth
12. In a DNA molecule, the number of nucleotides with guanine is 15% of the total. The proportion of nucleotides with thymine in this molecule will be
1) 15% 2) 35% 3) 45% 4) 85%
13. The human body is provided with ATP molecules in the process
1) oxygen stage of energy metabolism
2) preparatory stage of energy metabolism
3) synthesis of mRNA on DNA
4) protein synthesis using mRNA
During the embryonic development of a vertebrate animal, the primary cavity in the embryo is formed
1) during the formation of tissues
2) at the beginning of crushing
3) at the neurula stage
4) at the blastula stage
15. A wife with large eyes and a straight nose and a husband with small eyes and a Roman nose gave birth to children, some of whom had small eyes and a straight nose. Determine the genotypes of the parents if large eyes (A) and a Roman nose (B) are dominant traits.
1) ?ААБх^ааВВ
2) ?Aabbx^aaBb
3) ?Aabbx^aaBB
4) ?AaBbx^aaBb
16.Increasing the productivity of mold fungi that produce antibiotics is achieved by
1) polyploidization
2) intraspecific hybridization
3) mass selection
4) artificial mutagenesis
17.How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms?
1) the seeds are located inside the fruit
2) fertilization occurs in the ovules
3) seeds are formed as a result of fertilization
4) the embryo of the future plant is inside the seed
18.In the liver, excess glucose is converted into
1) glycogen 2) enzymes 3) adrenaline 4) hormones
19. Endocrine glands secrete hormones in
1) lymph 2) body cavities 3) blood 4) organ cells
B. The emergence of the class Insects, accompanied by an increase
the general level of their organization is an example of aromorphosis.
1) only A is correct
2) only B is correct
3) both judgments are correct
4) both judgments are incorrect
The scope of application of mushrooms is very wide. They are used both in the pharmaceutical industry and in food production.
Use of mushrooms in the food industry
Mushrooms are actively used in various areas of the food industry. They can be used:
- in winemaking;
- in bakery;
- in the production of cheeses and fermented milk products, various confectionery.
Despite the wide variety of modified yeast strains, the production of expensive wines (for example, French) still uses the live botrytis cinerea fungus, which causes grape rot.
In bread baking, special yeast is used, which gives the final product porosity. They enrich bread and bakery products with nutrients and microelements. In addition, at some factories they add “mushroom malt” to bread. This allows you to improve the taste of the products.
Mushrooms have found their use in clarifying fruit and berry juices. They secrete special enzymes that promote the decomposition of pectin substances.
It is worth noting that protease of fungal origin can be used in the meat processing industry. The addition of this substance makes the product less harsh and improves its taste.
“Mushroom malt” is actively used in the production of molasses and confectionery products. The substance slows down the process of sugar crystallization, which allows you to maintain an attractive presentation of products for a long time.
Use of mushrooms in the medicinal industry
Mushrooms are products that not only have high nutritional value, but also unique healing properties. That is why people in ancient times used them to get rid of various diseases. IN folk medicine Boletus mushrooms were used to treat frostbite.
Birch mushrooms have been used to relieve stomach problems. They are still sold in pharmacies in the form of a concentrated extract, which effectively fights gastritis and promotes the resorption of malignant tumors in the early stages.
In the modern world, mushrooms are used to make many other medicines. The discovery of antibiotics contributed to the rapid development of various branches of the pharmaceutical industry. Scientists conducted a series of studies during which antibacterial activity was identified in 3 thousand basidal fungi.
Today many preparations containing extracts are manufactured porcini mushroom. They are used to treat ulcers. The antibiotic porcini mushroom (herzenin) is actively used in the complex treatment of angina pectoris.
Antibiotic-containing mushrooms are used to produce medicines for tuberculosis, epilepsy and many other dangerous diseases. The pharmaceutical industry continues to develop at a rapid pace. Scientists are identifying new species of fungi that have medicinal properties. Many types of antibiotics they contain have not yet been fully studied. This suggests that mushrooms will continue to be used in the development and testing of new drugs.
Increasing the productivity of molds that produce antibiotics
Scientists have long been creating ways to increase the effectiveness of using mushrooms that have healing properties. Today, to solve this complex problem, the method of artificial mutagenesis is used.
It was discovered that the nature medicinal mushrooms can be modified by exposure to short-wave rays and various chemicals. This makes it possible to change the hereditary characteristics of mold fungi, as well as to develop new technologies that increase their productivity.
For example, the famous penicillium mushroom used to produce very little valuable substance (the antibiotic penicillin). But after scientists began to use artificial mutagenesis and learned to change the nature of penicillium, its productivity increased significantly.
Today, new hybrid forms produce 500 times more antibiotic than their predecessors, which were used 25-30 years ago.
Mushrooms for high cholesterol
Mushrooms - valuable product, containing trace elements that have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anti-cancer properties. They should become an integral element of the diet of any person who cares about their health.
Numerous studies have confirmed that regular consumption of certain types of mushrooms helps reduce blood cholesterol levels. Champignons and oyster mushrooms are the most effective in this regard. They contain a special substance, lovastatin, which slows down the processes of cholesterol synthesis in the liver. Mushrooms help get rid of cholesterol plaques in blood vessels.
Regular consumption of champignons in food helps cleanse the body, remove toxins and harmful wastes.
A healthy diet that definitely includes mushrooms is an excellent way to reduce the risk of developing:
- atherosclerosis;
- heart attack;
- stroke;
- oncology.
It is worth noting that you should not eat fried or canned mushrooms. To reduce blood cholesterol levels, it is worth steaming or stewing all food. Mushrooms can be baked with vegetables, boiled or dried. Such food strengthens the walls of blood vessels and is considered to prevent heart disease.
Champignons are a low-calorie product. It can be included in any diet. Despite low calorie content, mushrooms are high in protein, various vitamins and microelements.
If you have high cholesterol, you can drink the infusion kombucha. This must be done on an empty stomach. It is advisable to drink at least one liter of medicinal infusion per day.
Kombucha helps normalize lipid metabolism and also has an anti-inflammatory effect. It cleanses the body of harmful substances and toxins.
Mushrooms used in the food and medicinal industries will be presented at exhibition "Prodexpo", held annually at the Expocentre Fairgrounds.
In this article, I decided to continue publishing answers to the questions that biology students and tutors sent me and to which I responded in the comments.
Quite a few questions have accumulated and the comments take a long time to “scroll through”, but in the article they are placed more compactly.
I described how to most fully use tests compiled in the old way to prepare for passing the Unified State Exam. Therefore, the best basis for preparation is Open bank FIPI tasks, including KIM tests for all previous years and in our country.
1
.
Lichens do not belong to any of the kingdoms of living nature because they :
1) combine the characteristics of plants and animals
2) combine the characteristics of bacteria and animals
3) symbiotic organisms consisting of a fungus and algae
4) occupy an intermediate position between the kingdoms of plants and fungi.
It is difficult to say what answer the authors of this test had in mind, since lichens are “symbiotic organisms consisting of a fungus and an algae” that “occupy an intermediate position between the kingdoms of plants and fungi.” In my opinion, both of these answers are suitable as completely equivalent.
2
.
What causes the diversity of proteins:
1) the peculiarity of their primary structure
2) the presence of amino acids in their composition
3) the presence of peptide bonds
4) the ability to form hydrogen bonds.
The correct answer is 2) the presence of amino acids in their composition.
3
. The constancy of the number of chromosomes in the cells of one organism is ensured in the process:
1) gametogenesis
2) fertilization
3) mitosis
4) meiosis.
The correct answer is answer 3 - mitosis. Meiosis and gametogenesis followed by fertilization lead to a constant number of chromosomes in organisms from generation to generation during sexual reproduction.
4
.
What factor will lead to the disunity of individuals of the same species:
1) struggle for existence
2) genetic drift
3) insulation
4) mutation
5.
The correct answer is 3 - isolation.
Sexual reproduction, as opposed to asexual reproduction:
1) promotes the appearance of mutations
2) increasing adaptation to new living conditions
3) strengthening the characteristics of one of the parents
4) rapid growth in the number of individuals..
6
Mutagenic factors (chemicals, radiation), which cause mutations in the genetic material of the cells of organisms, “do not understand” how these organisms appeared sexually or asexually. With sexual reproduction, in contrast to asexual reproduction, there are chances of increasing combinative variability (as well as mutational variability, which is hereditary), which someday may lead to increased adaptation of organisms to new conditions. So the correct answer is 2
.
In animal breeding, individual selection is carried out to breed a pure line, taking into account:
1) genotype of the individual
2) the fertility of the individual
If the term “pure line” is used, then it does not matter at all what object is chosen for selection. The term pure line characterizes only the genotype of an organism, so the correct answer is 1.
7
. Pain receptors are formed from:
1) ectoderm
2) mesoderm
3) mesoglea
4) endoderm
Although pain receptors are located in the dermis, they are part of the nervous system, and the nervous system is formed from the ectoderm. So the correct answer is 1.
What mutations result in DNA with altered sequences of gene groups:
1) genetic
2) genomic
3) chromosomal
4) autosomal
If a mutation occurs not in one gene, but in a large section of a chromosome (in a group of genes), then the name of such a mutation is chromosomal. Answer 3.
8
. Increasing the productivity of mold fungi that produce antibiotics is achieved by:
1) polyploidy
2) intraspecific hybridization
3) mass selection
4) artificial mutagenesis
Correct answer 4 - by artificial mutagenesis.
9
. The role of the individual in the evolution of the species:
1) changing its phenotype
2) transmission of genes to descendants
3) the formation of combinative variability in it
4) the emergence of new modifications
Although combinative variability, like mutational variability, refers to a form of hereditary variability, in essence it does not provide the emergence of new characteristics. But even if answer 3) were about mutational variability, answer 2) should still be chosen. Since we are talking about the evolution of the species as a whole, no matter what beneficial mutations occur in the genotype of an individual, until it reproduces (that is, until it passes on its characteristics to its descendants), these mutations will not affect the evolution of the species in any way.
10
.
What is the role of cell engineering in plant breeding:
1) changes the timing of plant reproduction.
2) changes the phylogeny of valuable varieties
3) speeds up the time for breeding varieties
4) enhances the growth rate of organisms
11
The main role (direct role) of cell engineering in plant breeding is, of course, accelerating the development of new varieties. That is, the correct answer is 3). All other answers are equally suitable not only for the results of the use of cell engineering in breeding, but also for any traditional breeding methods.
. Are the judgments correct? 1. Living in communities different types
with the same needs leads to the formation of adaptations for mutually beneficial cohabitation.
2. The relationship between a squirrel and a moose living in the same forest is an example of mutually beneficial cohabitation.
2 is incorrect, this is an example of a neutral relationship.
12
. Methods of animal selection used in domestication include:
1) hybridization
2) individual selection
3) natural selection
4) interbreeding
There is some casuistry here among the compilers of this assignment. If by the domestication of animals by man we mean a process that has been going on since prehistoric times, then of course the correct answer is only 2. Man left for the tribe such animals whose characteristics satisfied him. Hybridization with subsequent selection is a modern stage of selection, the development of which became possible with the advent of the science of genetics.I have already stopped being “angry” with them. All the same, the authors of the questions are doing a great job - they have created thousands of test tasks. In such a huge “sea” of tests, one cannot do without flaws. The main thing is that all applicants are given equal conditions during the exams. That's why I'm more outraged by something else. After all, somehow, according to incorrect tests, approximately 150 people receive 100 points each year. I conclude that at least 150 times the “correct” answers are sold before exams.
13
. :
The formation of calcium deposits in the biosphere is associated with vital activity
1) arthropods
2) chemosynthetic bacteria
3) coral polyps
4) blue-green.
14
The answers are completely incorrect. Only bacteria (including blue-green bacteria) could have been involved in the deposition of calcium in the most ancient eras of the Earth. But we know (and this is the main thing in school textbooks) that limestone deposits (and these are the main deposits of calcium), reaching hundreds of meters, are the result of the activity of eukaryotic multicellular life forms - aquatic organisms that form their skeletons from lime. These are mainly coral polyps and mollusks. I think that the authors of this assignment have the correct answer 3.
.
Soil formation in the biosphere is associated with:
1) animals coming to land
2) development of land by autotrophic organisms
3) accumulation of silt in the hydrosphere
15
4) formation of an ozone screen
Answer 2) - the development of land by autotrophic organisms.
.
The tops of the main roots of cabbage seedlings are pinched to:
1) enhancing the growth of lateral roots
2) increasing the length of root hairs
16
.
In the process of life, organisms constantly change their habitat, which contributes to 1) the circulation of substances 2) the self-development of ecosystems
3) reproduction of organisms
4) growth and development of organisms
17.
It makes sense to talk about the cycle of substances associated with the activity of living systems only within the entire biosphere. When answering the question about “organisms in the process of their life,” it is hardly worth thinking so globally, but rather “descend” to the level of some community of organisms, the inhabitants of which “constantly change their habitat,” contributing to “2) the self-development of ecosystems” and gradual the replacement of one community by another.
What protein function is based on the ability of their molecules to change their structure:
1) energy
2) informational
3) contractile
4) storage
18.
Attention should be paid to “the ability of molecules to change their structure.” Answer 1) in principle is also suitable, but not only proteins, but any organic substances that enter the “furnace” of energy metabolism are broken down (which is impossible without changing the structure). If we assume that the question is about changes in the specific structures of only the protein, then answer 3) is the contractile function of myosin, for example, and is based on its conformational changes.
Red clover. occupying a certain area represents the level of organization of living nature:
1) Organic
2) Biocenotic
3) Biosphere
19. 4) Population-species
Does the action of stimuli cause the appearance of a nerve impulse in the bodies of sensory neurons or in the receptors of sensory neurons?
20 The action of stimuli causes the appearance of a nerve impulse (“production” of an electric current) in the receptors of sensitive neurons, and only then the nerve signal is transmitted along the axon of the sensitive neuron to its body.
.
21
The role of sexual selection in nature. Does it improve the gene pool of a population or contribute to the development of species characteristics?
The actual characteristics of the species are maintained by sexual reproduction in the course of natural selection. Based on the term “sexual selection,” in which males compete for a female based on the quality of their phenotype (and therefore better than other males of their genotype), we can conclude that this improves the gene pool of the population.
. The vaccine contains:
1) poisons secreted by pathogens
2) weakened pathogens
Of course, the term “vaccine” is both a drug obtained from weakened bacteria and viruses themselves, and a drug obtained from their metabolic products (toxoid). For example, toxoids are used to prevent diseases of tetanus, diphtheria, dysentery, and staphylococcal infection. Therefore, in this test, instead of one correct answer, three answers are given that are absolutely equally correct (all correct except the third answer).
22. In favorable conditions, bacteria multiply : 1) amitosis 2) sexually 3) budding 4) spores.
The difficulty in choosing the correct answer (amitosis) to this question lies in the fact that most often the term “amitosis” refers to the direct division of the interphase nucleus of an ordinary diploid eukaryotic cell by constriction without the formation of a division spindle or chromosome spiralization. And much less often, this term is used to characterize the division of a bacterial cell, which does not have a nucleus at all. Bacteria do not have true sexual reproduction at all (there is the possibility of recombination of part of the genetic material between two cells during conjugation). Yeasts reproduce by budding, and these are fungi - eukaryotes. Bacteria form spores, but this is not part of a cycle that serves for reproduction (as in fungi or plants), but only a way to endure unfavorable environmental conditions.
23 . As a result of mitosis, they are formed : 1) zygote in sphagnum 2) sperm in a fly 3) buds in an oak tree 4) eggs in a sunflower.
There is no doubt that the test is worthless. If you need to choose one answer, then the author of this test clearly has the answer : oak buds These are somatic diploid cells, for which the main method of division is mitosis (for old cells - amitosis). Unfortunately, this often occurs in test tasks, when their authors seem to completely forget that in plants spores undergo meiotic division, and the haploid germ cells (gametes) themselves are formed by mitosis from haploid spores, therefore answer 4) too should be considered correct.
24 .
Why is it important that during the process of mitosis there is an even distribution of chromosomes between daughter cells: 1) they contain hereditary information about the characteristics of the organism 2) chromosomes in body cells are paired 3) chromosomes include nucleic acids and proteins 4) chromosomes spiral in the process of mitosis.
25 .
Match the cells and the process associated with them. Select one or more answers. Zygote: a. Formed as a result of meiosis b. Diploid cells c. Formed as a result of mitosis d. Haploid cells e.
26. Subject to crushing f. :
The result of fertilization. Gametes: a. Result of fertilization b. Subject to crushing c. Formed as a result of meiosis d.
Haploid cells e. Formed as a result of mitosis f. Diploid cells
Zygote:
b, e, f.
Gamete: c,d (for plant cells the answer e is also suitable, since their gametes are formed from haploid spores by mitosis), but the authors of the questions probably completely “forgot” this.
27.
In animal cell mitosis, the nuclear envelope :
1) breaks up into separate membrane vesicles
2) dissolves and then assembles from individual molecules
3) disappears (broken down by enzymes) and then synthesized again
4) merges with the outer membrane and then separates from it
The difficulty in choosing an answer to this question is that it is written about this only in one of the 5-7 good school textbooks on General Biology. Of course, such too-deep-digging questions should not be included in test tasks at all (but every year there will be more and more such “dirty tricks”). By the way, this test is also incorrect because the answers 2) “dissolves” and 3) “disappears (split by enzymes)” are the same thing. The membrane consists of organic substances and it can “dissolve” only under the action of enzymes!
The diploid set of chromosomes in spinach cells is 12. As a result of induced mutagenesis, 4 mutant forms were obtained. Establish a correspondence between the karyotype of these forms and the type of genomic mutation as a result of which they were formed
Karyotype
A) 10
B) 11
B) 13
D) 48
28.
Genomic mutation :
1) trisomy
2) monosomy
3) mitosis
3) nullisomia
What did the authors of the question mean when they wrote “all human cells”? If they meant only human body cells (somatic cells), then the correct answer would be answer 3) mitosis But the sex cells are formed by meiosis - answer 4). Any human cells, both somatic and reproductive, are formed through reproduction - answer 1).
29 . The genotype of the organism is AaХВХВ. What types of gametes and in what ratio does this organism form when autosomes do not diverge in the first meiotic division? Indicate the number of chromosomes in them.
Since autosomes containing alleles A and a will not separate in anaphase of meiosis I, then after meiosis I there will be two cells with chromosomes consisting of two sister chromatids : the first cell is AAaaХBХB and the second cell is ХВХВ. After meiosis II, the first of these cells will give 2 gametes with chromosomes AaXB and AaXB, and the second will give 2 gametes with chromosomes XB and XB.
30. What number in the figure indicates the part of the tree stem in which growth rings are formed? (Indicate cambium or wood)
The cambium is a thin layer of living, constantly dividing meristematic cells. DUE to this, the growth of wood occurs, which we identify on the cut of the trunk by the growth rings. This means that each new growth ring is the result of the work of cambium cells, and the totality of all existing growth rings forms wood. Therefore, we can only guess what answer the authors of this question had in mind? The only good thing is that the question is drafted so incorrectly that probably any applicant who files an appeal will get the issue resolved in his favor.
*************************************************************************
Dear blog visitors, if you have any questions for the biology tutor via Skype, write in the comments.
You can purchase on my blog answers to all tests OBZ FIPI for all years of examinations and.